[SPRING] Spring의 기본 개념과 사용
Spring | Home
Cloud Your code, any cloud—we’ve got you covered. Connect and scale your services, whatever your platform.
spring.io
퀴즈 - 리눅스
기본 명령어 중심
캡처 - ubuntu - 각종 서버 + mybatis
putty - tomcat 실행 + 브라우저 화면
우분투 여러 서버 만든걸 mybatis코드 실행 시키고 putty에서 해당 서버 열고 tomcat실행? => 한 브라우저 화면 캡처?
리눅스
=> AWS영역
* 스프링
객체를 다루는 기술을 쉽게 만든다.
생성/할당/소거 = life cycle - spring framework
Spring DI(Dependency Injection)
사용 - 프로그래머
* 전처리 / 후처리 - Servlet Filter
Spring AOP(Aspect Orientation Programming)
=> Spring MVC(web)
Spring framework (중심)
Spring DI
Spring AOP
Spring MVC
=> 파생 프로젝트
Spring / Spring framework => Spring Boot
프로젝트 ( web / window ) 환경 구성
1. Java Project + 수동라이브러리
2. Maven / Gradle + 라이브러리 추가
방법1) Maven
방법 2) Java Project => Maven Project
3. Spring Boot
Spring DI(의존성 주입, 객체 조립기)
- 외부에서 두 객체 간의 관계를 결정해주는 디자인 패턴
- 약결합
IoC (Inversion of Control) - 제어의 역전
객체 조립
- xml (Spring Bean Configuration File)
- annotation + java
* Java project => maven project 변경
* pom.xml 내용 입력
* new(인스턴스 생성)를 spring에서 담당하게 된다.
<!--pom.xml-->
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.exam</groupId>
<artifactId>di</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>di</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<!-- Generic properties -->
<java.version>17</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<!-- Spring -->
<spring-framework.version>5.2.8.RELEASE</spring-framework.version>
<!-- Hibernate / JPA -->
<hibernate.version>5.6.9.Final</hibernate.version>
<!-- Logging -->
<logback.version>1.2.11</logback.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.36</slf4j.version>
<!-- Test -->
<junit.version>4.11</junit.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring and Transactions -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging with SLF4J & LogBack -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test Artifacts -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<release>11</release>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>* 객체의 생성 / 사용 / 소멸의 LifeCycle
//HelloBean1.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class HelloBean1 {
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+"님 안녕하세요");
}
}
//HelloBean2.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class HelloBean2 {
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello"+name);
}
}
//Main.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 객체 생성 / 사용 / 소멸
//생성
HelloBean1 hello1 = new HelloBean1();
//사용
hello1.sayHello("손수빈");
HelloBean2 hello2 = new HelloBean2();
hello2.sayHello("홍길동");
//소멸
hello1=null;
hello2=null;
}
}
=> 기본 생성 / 사용 / null로 소멸시킴
* 인터페이스로 호출
//Hello.java (interface)
package com.exam.di02;
public interface Hello {
void sayHello(String name);
}//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di02;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hello hello = new HelloBean1();
hello.sayHello("손수빈");
hello = new HelloBean2();
hello.sayHello("홍길동");
//메모리 제거기: 가비지 컬렉터
hello=null;
}
}+ HelloBean1.java , HelloBean2.java는 implements로 인터페이스를 참조
* Context.xml을 사용한 호출
//HelloBean1.java
package com.exam.di03;
public class HelloBean1 {
//생성자
public HelloBean1() {
System.out.println("HelloBean1 생성자 호출");
}
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+"님 안녕하세요");
}
}//HelloBean2
package com.exam.di03;
public class HelloBean2 {
//생성자
public HelloBean2() {
System.out.println("HelloBean2 생성자 호출");
}
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello"+name);
}
}//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di03;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource("D:\\Java\\spring-workspace\\DIEx01\\src\\com\\exam\\di03\\context.xml");
//해당 context를 읽는 순간에 인스턴스가 생성됨을 생성자 호출로 알 수 있다
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(resource);
//new(x) => 생성된 상태값만 가져옴
HelloBean1 hello1 = (HelloBean1)ctx.getBean("hello1");
hello1.sayHello("손수빈");
HelloBean2 hello2 = (HelloBean2)ctx.getBean("hello2");
hello2.sayHello("홍길동");
ctx.close();
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<bean name="hello1" class="com.exam.di03.HelloBean1" />
<bean name="hello2" class="com.exam.di03.HelloBean2" />
</beans>* 인터페이스 내용에서 bean이름을 다르게 설정하고 class내용을 HelloBean1으로 했을 때의 결과 확인
- Hello.java, HelloBean1.java, HelloBean2.java 내용 같음
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di04;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("D:\\Java\\spring-workspace\\DIEx01\\src\\com\\exam\\di04\\context.xml"));
Hello hello = (Hello)ctx.getBean("hello1");
hello.sayHello("홍길동");
hello=(Hello)ctx.getBean("hello2");
hello.sayHello("손수빈");
hello=(Hello)ctx.getBean("hello3");
hello.sayHello("빈수손");
ctx.close();
}
}<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<!-- HelloBean1 hello1 = new HelloBean1() -->
<bean name="hello1" class="com.exam.di04.HelloBean1" />
<bean name="hello2" class="com.exam.di04.HelloBean2" />
<bean name="hello3" class="com.exam.di04.HelloBean1" />
</beans>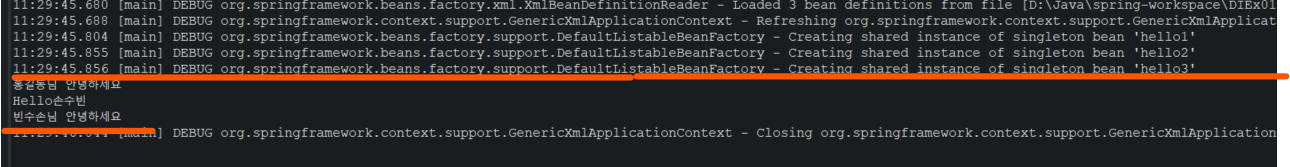
싱글톤(Singleton) 객체
- 생성자가 여러 차례 호출되더라도 실제로 생성되는 객체는 하나이고 최초 생성 이후에 호출된 생성자는 최초의 생성자가 생성한 객체를 리턴한다.
- 공통된 객체를 여러 개 생성해서 사용하는 DBCP(DataBase Connection Pool)와 같은 상황에서 많이 사용된다.
왜 사용하는가?
- 메모리 이점 : 한 개의 인스턴스만을 고정 메모리 영역에 생성하고 추후 해당 객체를 접근할 때 메모리 낭비를 방지
- 속도 이점: 생성된 인스턴스를 사용할 때는 이미 생성된 인스턴스를 활용하여 속도 측면에 이점이 있음
- 데이터 공유 쉬움: 전역으로 사용하는 인스턴스이기 때문에 다른 여러 클래스에서 데이터를 공유하며 사용할 수 있음.
다만 , 동시성 문제가 발생할 수 있어 유의하면 설계할 필요가 있음.
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di05;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("D:\\Java\\spring-workspace\\DIEx01\\src\\com\\exam\\di05\\context.xml"));
//new가 두번
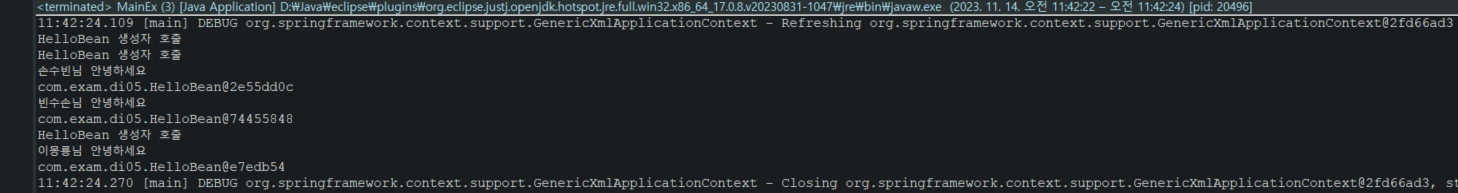
HelloBean hello11 =(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello11");
HelloBean hello12 =(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello12");
hello11.sayHello("손수빈");
System.out.println(hello11);
hello12.sayHello("빈수손");
System.out.println(hello12);
HelloBean hello13 =(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello11");
hello13.sayHello("이몽룡");
System.out.println(hello13);
//singletone 적용
HelloBean hello21 = (HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello21");
HelloBean hello22 = (HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello22");
System.out.println("hello21: "+hello21);
System.out.println("hello22: "+hello22);
//메모리 관리 용이
HelloBean hello23 = (HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello21");
System.out.println("hello23: "+hello23);
ctx.close();
}
}//HelloBean.java
package com.exam.di05;
public class HelloBean {
public HelloBean() {
System.out.println("HelloBean 생성자 호출");
}
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println(name+"님 안녕하세요");
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<!-- HelloBean1 hello1 = new HelloBean1() -->
<bean name="hello11" class="com.exam.di05.HelloBean" scope="prototype"/>
<bean name="hello12" class="com.exam.di05.HelloBean" scope="prototype"/>
<bean name="hello21" class="com.exam.di05.HelloBean" scope="singleton"/>
<bean name="hello22" class="com.exam.di05.HelloBean" />
</beans>


기본생성자 기본 호출
//HelloBean.java
package com.exam.di06;
public class HelloBean {
private String name;
//default 생성자
public HelloBean() {
System.out.println("HelloBean() 생성자 호출");
this.name="홍길동";
}
//오버로딩 생성자
public HelloBean(String name) {
System.out.println("HelloBean(String name) 생성자 호출");
this.name=name;
}
public HelloBean(String firstname, String lastname) {
System.out.println("HelloBean(String firstname, String lastname) 생성자 호출");
this.name=lastname+" "+firstname;
}
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(name+"님 안녕하세요");
}
}//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di06;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di06/context.xml"));
HelloBean hello1=(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello1");
hello1.sayHello();
HelloBean hello2=(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello2");
hello2.sayHello();
HelloBean hello3=(HelloBean)ctx.getBean("hello3");
hello3.sayHello();
ctx.close();
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<!-- default생성자 호출 -->
<bean name="hello1" class="com.exam.di06.HelloBean" scope="prototype"/>
<bean name="hello2" class="com.exam.di06.HelloBean" scope="prototype">
<!-- <constructor-arg> -->
<!-- <value>손수빈</value> -->
<!-- </constructor-arg> -->
<constructor-arg value="빈수손"/>
</bean>
<bean name="hello3" class="com.exam.di06.HelloBean" scope="prototype">
<!-- <constructor-arg> -->
<!-- <value>SOOBIN</value> -->
<!-- </constructor-arg> -->
<!-- <constructor-arg> -->
<!-- <value>SON</value> -->
<!-- </constructor-arg> -->
<!-- 순서 중요 (파라미터 순서) -->
<constructor-arg value="SOOBIN" index="0"/>
<constructor-arg value="SON" index="1"/>
</bean>
</beans>Setter 메서드 방식
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di01;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di01/context.xml"));
WriteAction writeAction1=(WriteAction)ctx.getBean("writeAction1");
System.out.println(writeAction1);
WriteAction writeAction2=(WriteAction)ctx.getBean("writeAction2");
System.out.println(writeAction2);
ViewAction viewAction1=(ViewAction)ctx.getBean("viewAction1");
System.out.println(viewAction1);
viewAction1.execute();
ctx.close();
}
}
//BoardTO.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class BoardTO {
public BoardTO() {
System.out.println("BoardTO()호출");
}
}
//ViewAction.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class ViewAction {
private String seq;
private BoardTO to;
public ViewAction(String seq, BoardTO to) {
System.out.println("ViewAction(String seq, BoardTO to) 호출");
this.seq=seq;
this.to=to;
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println(seq);
System.out.println(to);
}
}
//WriteAction.java
package com.exam.di01;
public class WriteAction {
private BoardTO to;
public WriteAction() {
System.out.println("WriteAction() 생성자 호출");
this.to = new BoardTO();
}
//오버로딩
public WriteAction(BoardTO to) {
System.out.println("WriteAction(BoardTO to)생성자 호출");
this.to =to;
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<bean name="writeAction1" class="com.exam.di01.WriteAction"/>
<bean name="to1" class="com.exam.di01.BoardTO"/>
<bean name="writeAction2" class="com.exam.di01.WriteAction" scope="prototype">
<!-- <constructor-arg ref="to1"/> 참조형식 -->
<constructor-arg>
<!-- 참조x , 아예 집어넣기 -->
<bean class="com.exam.di01.BoardTO" scope="prototype" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean name="viewAction1" class="com.exam.di01.ViewAction">
<constructor-arg value="1"/>
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="com.exam.di01.BoardTO" scope="prototype"/>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>lombok 사용
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di02;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di02/context.xml"));
ListAction listAction = (ListAction)ctx.getBean("listAction");
listAction.execute();
ctx.close();
}
}
//BoardTO.java
package com.exam.di02;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class BoardTO {
private String seq;
private String subject;
}
//ListAction.java
package com.exam.di02;
public class ListAction {
private BoardTO to;
public ListAction(BoardTO to) {
System.out.println("ListAction(BoardTO to) 생성자 호출");
this.to = to;
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<bean name="to" class="com.exam.di02.BoardTO" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg value="1" />
<constructor-arg value="제목 1" />
</bean>
<bean name="listAction" class="com.exam.di02.ListAction" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg>
<ref bean="to" />
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
@AllArgsConstructor
- 자동으로 모든 필드에 대한 생성자를 순서대로 생성하는 데 사용.
- TO 클래스에서 적용하면, 해당 클래스의 모든 필드를 인자로 받는 생성자가 자동으로 생성됨.
- 코드상 필드 순서를 바꿔도 적용되지 않아 실제 넣고 싶은 값이 잘못들어갈 수 있음 (@Builder로 유연하게 사용 가능)
추가로...
@NoArgsConstructor
- 파라미터가 없는 기본 생성자를 생성
- final 필드가 있는 경우 Compile Error발생
객체의 주입을 통한 set
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di03;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di03/context.xml"));
BoardTO to =(BoardTO)ctx.getBean("to");
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
WriteAction writeAction1=(WriteAction)ctx.getBean("writeAction1");
writeAction1.execute();
//to.setSeq("2");
//System.out.println(to.getSeq());
WriteAction writeAction=(WriteAction)ctx.getBean("writeAction2");
//System.out.println(writeAction);
writeAction.execute();
ctx.close();
}
}
//BoardTO.java
package com.exam.di03;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Setter
@Getter
public class BoardTO {
private String seq;
private String subject;
}//WriteAction.java
package com.exam.di03;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WriteAction {
private BoardTO to;
public void execute() {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 프로퍼티 통한 주입 -->
<bean name="to" class="com.exam.di03.BoardTO" scope="prototype">
<property name="seq" value="1"/>
<property name="subject" value="제목1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="writeAction1" class="com.exam.di03.WriteAction">
<constructor-arg ref="to"/>
</bean>
<bean id="writeAction2" class="com.exam.di03.WriteAction">
<constructor-arg>
<bean class="com.exam.di03.BoardTO" scope="prototype">
<property name="seq" value="2"/>
<property name="subject" value="제목 2"/>
</bean>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>Setter / Getter
xmlns:p 사용하기
//MainEx.java
package com.exam.di04;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di04/context.xml"));
BoardTO to =(BoardTO)ctx.getBean("to");
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
to.setSeq("2");
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
ctx.close();
}
}
//BoardTO.java
package com.exam.di04;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Setter
@Getter
public class BoardTO {
private String seq;
private String subject;
}
//WriteAction.java
package com.exam.di04;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WriteAction {
private BoardTO to;
public void execute() {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
}<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 이름공간 : 네임스페이스 p -->
<bean name="to" class="com.exam.di04.BoardTO" p:seq="1" p:subject="제목 1" scope="prototype"/>
</beans>기존 JAVA코드로 했던 복잡한 초기화..
//MainEx01.java
package com.exam.di05;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MainEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Bean Configuration File에서 처리
ArrayList<String> userLists = new ArrayList();
userLists.add("손수빈");
userLists.add("홍길동");
BoardListTO listTO = new BoardListTO();
listTO.setUserLists(userLists);
for(String user: listTO.getUserLists()) {
System.out.println(user);
}
ArrayList<BoardTO> boardList = new ArrayList();
BoardTO to1=new BoardTO();
to1.setSeq("1");
to1.setSubject("제목1");
BoardTO to2=new BoardTO();
to2.setSeq("2");
to2.setSubject("제목2");
boardList.add(to1);
boardList.add(to2);
listTO.setBoardLists(boardList);
for(BoardTO to : listTO.getBoardLists()) {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
}
}//BoardTO.java
package com.exam.di05;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Setter
@Getter
public class BoardTO {
private String seq;
private String subject;
}//BoardMapTO.java
package com.exam.di05;
import java.util.HashMap;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class BoardMapTO {
private HashMap<String, String> userMaps;
private HashMap<String, BoardTO> boardMaps;
}//BoardListTO.java
package com.exam.di05;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
public class BoardListTO {
private ArrayList<String> userLists;
private ArrayList<BoardTO> boardLists;
}Context.xml로 UserList 출력
//MainEx02.java
package com.exam.di05;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//context.xml을 통해 초기화와 출력 작업을 한다. (MainEx01.java와 비교)
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di05/context.xml"));
BoardListTO listTO =(BoardListTO)ctx.getBean("listTO");
for(String user: listTO.getUserLists()) {
System.out.println(user);
}
for(BoardTO to: listTO.getBoardLists()) {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
ctx.close();
}
}
//MainEx03.java
package com.exam.di05;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
public class MainEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(new FileSystemResource("./src/com/exam/di05/context.xml"));
BoardMapTO mapTO=(BoardMapTO)ctx.getBean("mapTO");
for(String key: mapTO.getUserMaps().keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
for(String value: mapTO.getUserMaps().values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
for(String key: mapTO.getBoardMaps().keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
for(BoardTO to: mapTO.getBoardMaps().values()) {
System.out.println(to.getSeq());
System.out.println(to.getSubject());
}
ctx.close();
}
}
<!--context.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="to1" class="com.exam.di05.BoardTO">
<property name="seq" value="1" />
<property name="subject" value="제목 1" />
</bean>
<bean id="to2" class="com.exam.di05.BoardTO">
<property name="seq" value="2" />
<property name="subject" value="제목 2" />
</bean>
<bean id="listTO" class="com.exam.di05.BoardListTO" scope="prototype">
<property name="userLists">
<list>
<value>홍길동</value>
<value>손수빈</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="boardLists">
<list>
<ref bean="to1" />
<ref bean="to2" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="mapTO" class="com.exam.di05.BoardMapTO" scope="prototype">
<property name="userMaps">
<map>
<entry key="key1">
<value>손수빈</value>
</entry>
<entry key="key2">
<value>홍길동</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="boardMaps">
<map>
<entry key="key1">
<ref bean="to1" />
</entry>
<entry key="key2">
<ref bean="to2" />
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>